PE Water Supply Pipe
Product Introduction:
PE water supply pipe is a type of piping made from polyethylene (abbreviated as PE) as the raw material. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, it is widely used in water supply projects, particularly in municipal water supply, agricultural irrigation, and industrial drainage systems.
Product Features:
The primary material of PE water supply pipes is polyethylene, which offers high strength, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, non-toxicity, and wear resistance. These characteristics make PE pipes an ideal replacement for traditional metal pipes (such as iron pipes), especially in applications requiring corrosion resistance and long-term durability.
Product Applications:
- Municipal Underground Water Supply– PE water pipes are suitable for urban water supply networks, providing clean and stable water sources.
- Building Water Supply & Drainage– In the construction industry, PE pipes are used for indoor and outdoor water supply and drainage systems.
- Agricultural Irrigation– PE pipes are used in drip irrigation, sprinkler systems, and drainage, improving water resource efficiency.
- Industrial Use– PE pipes are widely applied in industrial water transportation, drainage, and sewage systems.
Product Performance Indicators:
- Elongation at Break
Elongation at break is a key indicator of PE pipe flexibility, reflecting its adaptability to uneven ground settlement and seismic resistance. National standards require an elongation at break ≥350%, while high-quality PE pipes can exceed 700% in testing. - Longitudinal Reversion Rate
This measures dimensional stability under thermal influence, indicating deformation after heating. The standard requires ≤3% to ensure minimal size changes during installation and use. - Oxidation Induction Time (OIT)
OIT evaluates thermal stability and anti-aging performance, directly correlating with long-term heat resistance. It measures the time before autocatalytic oxidation begins under high temperatures, assessing material durability. - Pressure Resistance
A critical technical parameter, PE water pipes are classified into six pressure grades per GB/T 13663-2000: 0.4 MPa, 0.6 MPa, 0.8 MPa, 1.0 MPa, 1.25 MPa, 1.6 MPa (PE100 pipes, max. 16 kg/cm²).
Pressure tests are conducted at 5× working pressurefor 24 hours to ensure reliability. - Temperature Derating Factor
For PE piping systems operating continuously above 20°C, the Maximum Operating Pressure (MOP) is adjusted using a temperature derating coefficient to maintain pressure resistance in high-temperature environments. - Physical Performance Metrics
The physical performance indicators of PE water supply pipes also include hydrostatic strength at various temperatures, elongation at break, longitudinal reversion rate, etc. For example, the hydrostatic strength of PE water supply pipes at 20°C (i.e., hoop stress of 9.0 MPa) must ensure no cracking or leakage after 100 hours; at 80°C (hoop stress of 4.6 MPa), the pipes must withstand 165 hours under these conditions.
Product Specifications:
Pipe Connectors:
The main connection methods for pipes are
① For DN≤63, use socket fusion (heat fusion) or electrofusion connections;
② For DN≥75, butt fusion (heat fusion) or electrofusion connections are preferred;
③ For connections to metal pipes and pipe accessories, flange connections or transition fittings can be used.
Socket Fusion Connection
When using this method, a socket fusion welding machine is employed. The specific steps are as follows:

① Check the pipe surface quality. The connection area should be clean, free of cracks, smooth, flat, and without burrs.
② Measure the socket depth and mark the insertion line clearly on the pipe surface.
③ Use a special scraper to treat the pipe’s connection surface, ensuring a fresh layer all around. Bevel the pipe end if needed; the bevel angle should be 30°, and the bevel length should not exceed 2.0 mm.
④ Wipe the socket surface of the fitting with a dry cloth to ensure it is clean and free of debris.
⑤ Insert the pipe and fitting—without rotating—into the heating tool at the same time and heat the joint area.
⑥ Once the heating time is reached, quickly and evenly remove the pipe and fitting from the heater and push the pipe into the socket in one smooth motion, forming a raised bead around the joint.
⑦ Allow the pipe and fitting to cool completely for the specified time before performing the next operation.
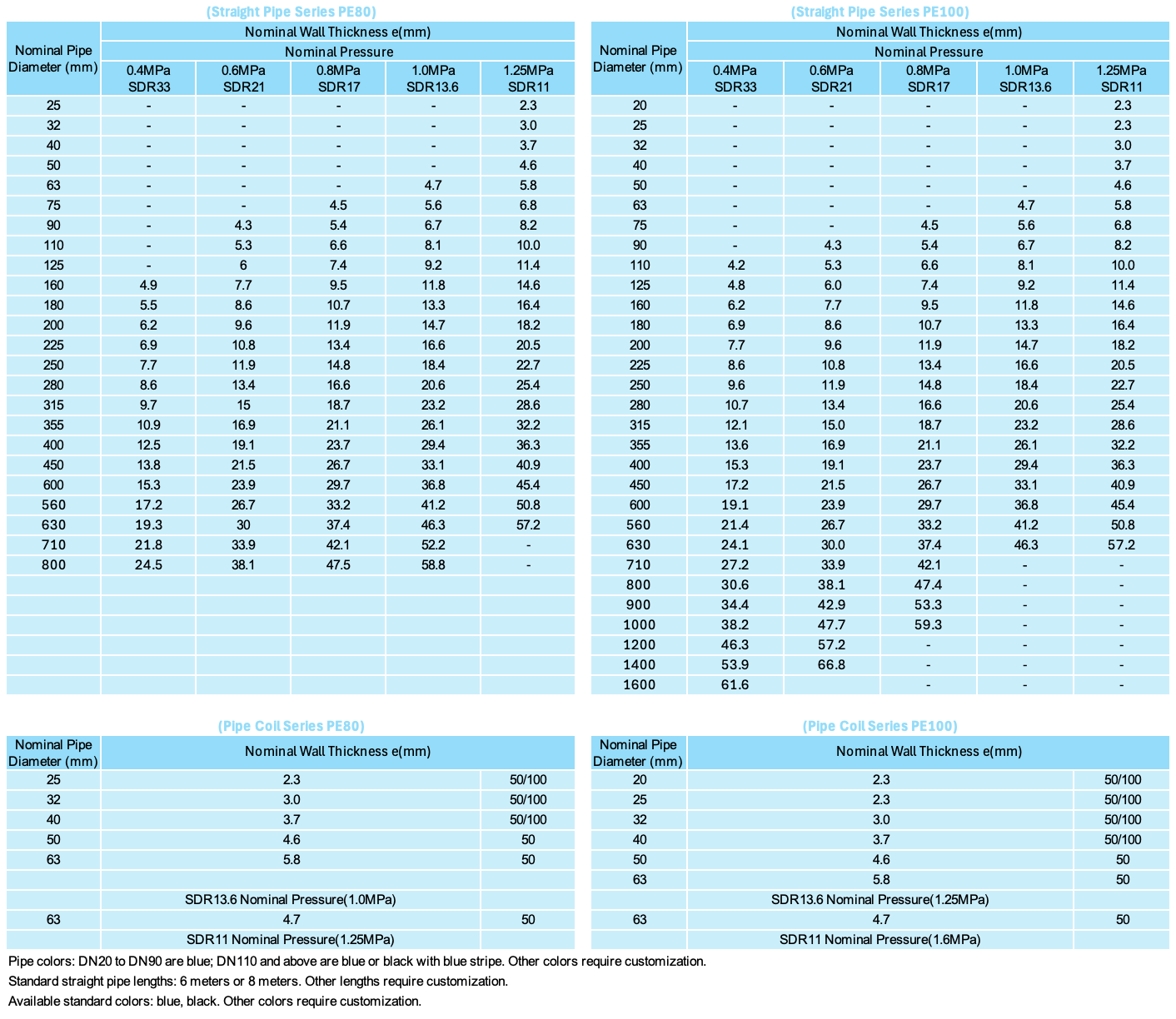
Butt Fusion

When using this connection method, a butt fusion welding machine shall be employed. The specific procedures are as follows:
① Prepare all required tools.
② Secure the pipes in the welding machine fixtures, clean and mill the connection ends, align the pipes, ensuring offset does not exceed 10% of wall thickness.
③ Insert the heating plate.
④ After heating, remove the heating plate, promptly join the heated surfaces, increase to fusion pressure and maintain pressure during cooling.
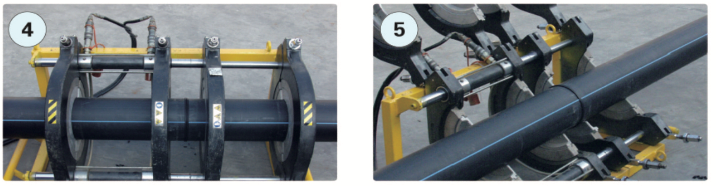
⑤ Fusion completedElectrofusion Connection
Electrofusion socket connection features convenient and rapid joining, minimal external interference, and offers economic advantages for small-diameter pipelines (DN≤63) or in challenging construction scenarios. Connection schematic is shown below:

① Clean contaminants from the pipe connection surface and mark the insertion depth.
② Remove the surface oxide layer.
③ Slide the electrofusion fitting onto the pipe, ensuring proper alignment on the same axis.
④ During electrified heating, a small amount of molten material should visibly push out from the inspection port.
⑤ Allow the joint to cool naturally to complete the electrofusion process.Precautions: During connection, the selected voltage and heating time for electrified heating must comply with the specifications of the electrofusion equipment manufacturer. During the cooling period of electrofusion, do not move the connected parts or apply any external force to them.
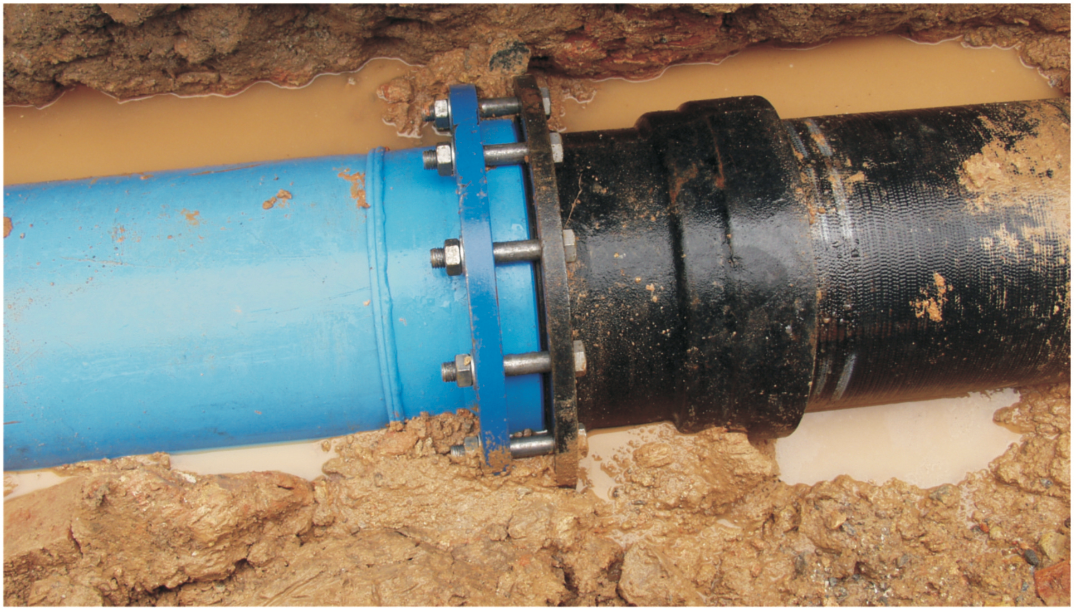
Transition Connection
For connections between pipes and metal pipes/pipeline accessories (such as valves, water meters, etc.), threaded or flanged transition fittings shall be used at the joint interfaces.

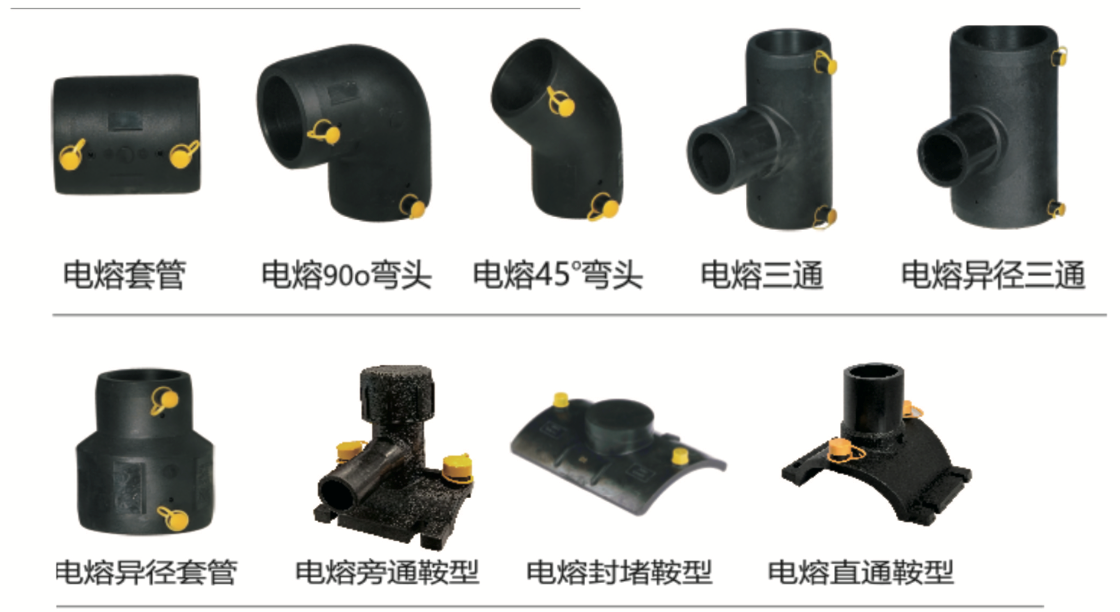
Pipe Fittings Series:
Injection-Molded Socket Fittings: Injection-molded fittings are blue or black in color for sizes DN20 to DN90. For DN110 and above, they are also available in blue or black. Color options: Blue, Black.

Injection-Molded Butt Fittings:
Injection-molded fittings are blue or black for sizes DN20 to DN90. For DN110 and above, they are also blue or black. Color options: Blue, Black.
Electrofusion Fittings: Electrofusion fittings are black in color.
